Pitch Registration and Harmonic Fields in Works of Pierre Boulez, Marco Stroppa, and Yukiko Watanabe
Simon Tönies
KEYWORDS: Pierre Boulez, Marco Stroppa, Yukiko Watanabe, Albert Bregman, Jean-Louis Leleu, pitch registration, harmonic field analysis, serial music, psychoacoustics
ABSTRACT: This paper discusses a method for harmonic field analysis of serial and post-serial music. The method is informed by perception-oriented considerations and was specifically designed for an analysis of Pierre Boulez’s early serial music. It is therefore exemplified by his 1951 composition Polyphonie X. Harmonic field analysis can however be applied to any music where pitch registration plays an important role. Accordingly, I will provide a brief overview of harmonic relations in two more recent compositions by Marco Stroppa and Yukiko Watanabe, demonstrating that harmonic fields have been used by composers to mediate between the generative layers of pitch organization and the sounding surface.
DOI: 10.30535/mto.30.2.7
Copyright © 2024 Society for Music Theory
0. Introduction
[0.1] It is a dialectical situation: any separation between “structural” and “formal” qualities of a piece is artificial and provisional.(1) Music theorists know how closely the two domains are linked together and how problematic a distinction between them can be. But then again, assuming they are the same seems equally problematic. Serial and algorithmic music is sometimes criticized for its distinction between structure- and form-oriented compositional strategies. According to these critics, the organizational or generative procedures typical for this kind of music (which usually precede work on the actual score or soundscape) are meaningless in the sense that they cannot be perceived as part of the formal discourse.(2) For example, in an article on musical time, Gérard Grisey (1987) attacks a number of twentieth-century composers for applying organizational principles without closely considering the sounding outcome. Grisey (1987, 240) argues that such “speculations” end up “confusing the map with the lie of the land,” creating an artificial sphere that is separated from the composition itself. On a similar note, Fred Lerdahl (1992, 119) critically discusses Pierre Boulez’s (1925–2016) serial composition Le Marteau sans maître and concludes with a normative claim: “The best music arises from an alliance of a compositional grammar with the listening grammar.” The ideal behind these viewpoints seems to be identity: complete transparency of all generative and organizational principles to the listener as such, structure becoming form.
[0.2] In my opinion, such a perspective is reductionist on several levels. First, it arbitrarily reduces the complexity of an artistic practice to only one of many possible spaces: a composer subject who controls and shapes the listening experience via musical form. Second, it reduces the varied, mediated, and dynamic interconnections between different organizational layers to only those that are directly intelligible for the composer as well as the listener. And finally, it reduces the listening experience to a reconstruction of the compositional process. Alternatively, I would argue that each organizational principle applied to a piece of music to constitute “structure” is what one could call, following Bruno Latour (2005), an actant in a complex network that influences the sounding result with its potentials for perception as well as further compositional decisions.(3) In such a network, structure is neither identical with nor separated from the sounding result but dynamically entangled with it.
[0.3] These organizational principles act on different layers regarding the subjective agency of the composer: they can be closer to the surface and more controllable, or they can operate on a more mediated, less controllable layer. In serial music, the more hidden layers obviously play an important role. At the same time, the fact that protagonists often marginalized them as something that precedes the “actual composition”(4) shows that compositional agency toward the sounding result, in which an important task of the composer is arranging material in an audibly meaningful way, remains an essential concept.
[0.4] The distribution of pitches in register is an organizational structure that is relatively close to the surface layer. It has an immediate effect on the sounding result but can also deliberately reflect certain underlying organizational or generative structures.(5) For analysis of music that makes use of these structures, we require a method that systematically takes pitch registration into account. The method I will propose in this article can be described as a more perception-oriented take on Jean-Louis Leleu’s (2015) field analysis, shifting the focus from interval cycles to auditory streams and statistical interval accumulations. It was specifically designed for an analysis of Pierre Boulez’s (1925–2016) early serial composition Polyphonie X and will be presented using this composition as an example. But the method can be applied to any work of serial or post-serial(6) music where pitch registration plays an important role. In this spirit, I will provide a brief overview of harmonic relations in two more recent compositions by Marco Stroppa (1959–) and Yukiko Watanabe (1983–).
1. Methodology
[1.1] In his famous analysis of Boulez’s Structure Ia, György Ligeti (1958, 56–63) illuminates how the partial fixation of pitch registers, above a certain polyphonic density, leads to nodes in the form of repeated notes and intervals, and how, in this way, the space between decision (registration) and automatism (coincidence of serial forms) is made productive. But although Ligeti says that decision and automatism are not opposing principles, he treats them as such throughout the essay. Robert Piencikowski (1985) corrects this by illuminating the connections between register choice and serial structure. From an analysis of some of Boulez’s works, Piencikowski concludes that pitch registration is used by Boulez to bring certain characteristics of the serial structure to the sounding surface.(7)
[1.2] While Piencikowski’s merit is to tie Ligeti’s observations in pitch registration back to the serial structure of a piece, Christian Utz (2017; 2013; 2012) attempts an approach from the other side by delving into the interplay between auditory selection processes and register-related grouping mechanisms from a perceptual-psychological perspective. Taking into account the perceptual level, the interval nodes observed by Ligeti become, in Utz’s terms, gestalt-like, since the listener prefers to group them and connect tones with similar frequencies to each other even if they do not immediately follow one another.(8) According to Utz (2017, 4), these “gestalt nodes” can support hearing, even if they are not identified in an “analytical-rational sense” during listening.
[1.3] The idea of gestalt nodes—I prefer to call them constellations—brings Ligeti’s analysis together with Albert S. Bregman’s theory of auditory streaming. Bregman states that we group acoustic information according to the principle of similarity and perceive such groups as separate entities. Bregman’s observation is that the components of a group can be arranged discontinuously (1994, 47): “In this phenomenon the auditory system is grouping tones that are similar to one another in preference to grouping tones that follow one another immediately in time.” An important distinguishing feature or “cue” in Bregman’s theory is pitch. From experiments Bregman concludes that, in principle, those pitches are associated that are closest to each other in frequency (65). Later studies by several research groups have confirmed this assumption.(9)
[1.4] If a harmonic analysis of register movements can make use of these insights, then it can only do so within narrow limits. It can neither predict how exactly a particular passage is perceived—that would require a completely different, empirically oriented experimental set-up—nor do full justice to the complex interplay of disparate stimuli.(10) What it reveals are structures of pitch organization, not structures of the listener’s brain. Pitch structures characterize a piece and its poetics without necessarily being directly apparent to the listener. But at the same time, they also contain identifiable perceptual potentials. My aim is therefore to propose an analytical approach that takes the auditory level into account as a potential. This approach is oriented toward small intervals arising through pitch registration. With this orientation, it can record statistical fluctuations that might influence the perception of form.
[1.5] Jean-Louis Leleu’s field analysis is useful for this purpose. Leleu conceives more or less consistent and delimitable registral distributions (primarily of the twelve chromatic pitch classes) as harmonic fields that can extend over short passages to whole sections of a piece. Using Boulez’s Livre pour quatuor as an example, Leleu demonstrates the organic transitions between such fields: “It is interesting to see
[1.6] Leleu chooses a representation where the registered pitches of a given passage are placed in ascending order. In addition, each frequency has a fixed horizontal position so that identical pitches between several successive, vertically stacked field representations will share the same column. I will adopt this method of representation in examples to follow. Due to its proportionality, it allows a quick overview of the characteristics of the fields. Spread or compression, relative height or lowness in frequency, and homogeneity or heterogeneity within and between the fields can be read at a glance.
[1.7] I use the following systematic procedure to extract the harmonic fields from a given score:
- Numbering every note with its corresponding pitch class number from 0 (C) to 11 (B);
- Tracing each octave shift on the bottom of the page by noting the respective pitch class;
- Identifying harmonic fields of relative consistency (ideally: no octave shifts within a field).
[1.8] Of course, the delimitation of the fields leaves room for interpretation. In Boulez, there are often clusters of register changes at the beginning of a field, which then remains constant for several bars and thus causes no problems with delimitation. Sometimes only one or two notes change quickly back and forth between the registers—in this case, I typically assume a single field (with some internal mobility) instead of many static, chromatically incomplete fields. In the Examples, I mark such octave shifts via horizontal dashes. If a note only appears within the transition between two fields (like the
[1.9] To illustrate internal structures in his analytic reductions, Leleu connects groups of notes with beams. By doing so, he identifies and reveals interval cycles, continuing the work of George
2. Harmonic field analysis in the first movement of Pierre Boulez’ Polyphonie X (1951)
Example 1. Henri Pousseur, Trois chants sacrés, transcription of the end of the second movement
(click to enlarge)
[2.1] Already as a young composer, Boulez was intuitively aware of the grouping and selection mechanisms outlined above. In a letter from March 1952, he replies to his colleague Henri Pousseur, who had been worrying about a latent C minor connection in the second piece of his Trois chants sacrés (see Example 1): “Votre impression d’accord d’ut mineur à la fin n’est que visuelle, car l’oreille entend plutôt le rapport [D3–G3–
[2.2] For Boulez the choice of pitch registers is a privileged field in which the composer can play with such perceptual potentials.(15) In this function, pitch registration is far more than just a means of avoiding octaves. Instead, strategies like a constant interplay between fixed and mobile register positions become a central aesthetic idea. Boulez ([1952] 1991, 119–120) states:
There are many kinds of interference to be set up between the series itself and the register, on the basis that either of these two elements can be mobile or immobile in relation to the other. One has only to imagine the instability arising out of the relation between an unchanging series and a continuously changing register, or between changing series and a completely fixed register: the extreme points in the play of ambiguities of pitch, which may equally combine with ambiguities of rhythm or dynamics.
[2.3] Without making it explicit, this quotation describes the compositional method of Boulez’s unfinished Première Polyphonie (1950) with some precision. This work was planned to be the first of a series of compositions that explore the concept of polyphony—a project that due to its ambitious scale was quickly abandoned for the more manageable Polyphonie X (1951).(16) The beginning of this first version, Première Polyphonie, realizes the model of a relatively fixed pitch network for a multitude of rows running in parallel. In later sections in which only one row at a time is processed with different transpositions, movement between different registers accelerates.(17)
[2.4] In Polyphonie X, too, the registral distributions can be grouped into harmonic fields with varying stability. The following analysis will focus on the aspect of interval convergence (the accumulation of certain small intervals). It can be assumed that interval convergence within the fields influences the sounding result and its perception. For this reason, special attention is paid to recurring intervals and their strategic positioning (for example in the extreme positions). In a second step, I will examine how the harmonic fields relate to more hidden, row-specific background structures.
[2.5] The pitch registration of the first movement of Polyphonie X follows the dramatic principle of “[a]grégation et désagrégation” that Boulez already mentions in the early sketches.(18) In concrete terms, a gradual crystallization and dissolution of the tritone interval can be observed. Four stages are distinguishable and can be traced in various sections(19) of the movement:
- interval heterogeneity or avoidance of intervals in close positions;
- convergence of minor and major thirds;
- superimposition of (minor) thirds and tritones;
- convergence of tritones.
Example 2. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, harmonic fields mm. 10–15; the pitch registration causes a gradual detachment of the tritone from the minor third
(click to enlarge)
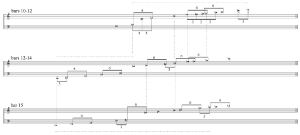
[2.6] The first fifteen bars up to the duet of the second violin and cello in m. 16 develop along these stages of interval heterogeneity to a predominance of third and finally tritone constellations. In the process, the gradual convergence of third and tritone intervals coincides with an increasing polyphonic density and, at the same time, with a shift to the lower registers. Example 2 affords us a closer look at the three harmonic fields in mm. 10–15.
[2.7] As one can see, the register dispositions are relatively unstable, with only one pitch class (B) remaining in a single octave position over the whole six bars and two or three additional pitch classes that stay in their position between two fields (see vertical dashed lines). On top of that,
Example 3. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, mm. 10–15 (score in C), facsimile of the fair copy in the SWR Notenarchiv Baden-Baden, D 4098
(click to enlarge)
[2.8] A look at the realization of this harmonic potential in the score (Example 3) shows an accumulation of melodic tritone successions in the individual voices, which result from two tritone segments in the underlying tone row. The tritone is particularly prominent in m. 15 with an E6–
Example 4. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, harmonic fields mm. 30–32
(click to enlarge and see the rest)
[2.9] The four stages of interval convergence are then immediately repeated with the solo interlude (mm. 16–23) representing stages 1 and 2 and the second, more polyphonic part of this first section (mm. 24–49) returning to stages 3 and 4. The focal point of this second tritone convergence coincides with the entry of the first woodwind group in m. 32. As shown in Example 4, the harmonic field of mm. 30 and 31 prepares it. The first field already contains three tritone connections, two of them resulting from a cycle of thirds in the middle, one at the upper edge of the field. The cross-movement of
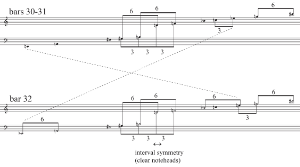
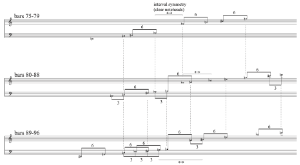
[2.10] As if under a microscope, the slow Assez lent sections of the first movement seem to anatomize the harmonic processes that have been established at the beginning of the piece. For example, the first of these slow sections (mm. 75–96)(21) places the intervals
Example 5. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, mm. 75–77 (score in C), tritone “imitations” in oboe, flute, trumpet and first violin (click to enlarge) | Example 6. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, mm. 78–80 (score in C), tritone “imitations” in clarinet, oboe, flute and first violin (click to enlarge) |
[2.11] Additionally, a striking instrumentation effect accompanies the tritone harmony in this section: the instruction “laisser rebondir l’archet” (“let the bow rebound”) in the third string section creates noisy, flickering impact curves (see the score in Example 10 below, mm. 75–80). Interestingly, the return of this effect toward the end of the section (m. 90) coincides with a reestablishment of the tritone after the polar thirds A2–C3 (Example 7, mm. 79–81, tuba, bass clarinet, cello I) and
Example 7. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, mm. 79–81 (score in C), low-registral minor third “imitations” in clarinet, trombone and first cello (click to enlarge) | Example 8. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, mm. 82–85 (score in C), high-registral minor third “imitations” in piccolo flute, oboe and trumpet (click to enlarge) |
[2.12] In Example 9, this harmonic process can be traced: the final field places all six possible tritones in close position. The structural principle in creating these fields seems to be a symmetrical interval distribution—as in the previous example, most notes are symmetrically arranged around a central interval.
Example 9. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, harmonic fields of the first Assez lent section (mm. 75–96). (click to enlarge) | Example 10. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, first movement, mm. 75–80 (score in C), facsimile of the fair copy in the SWR Notenarchiv Baden-Baden, D 4098 (click to enlarge and see the rest) |
[2.13] On the one hand, the tritone harmony in Polyphonie X result from artistic choices of the composer. Boulez shapes the material generated by a complex set of algorithms by means of harmonic fields that in turn influence the sounding outcome.(22) But it would be wrong to consider such efforts as completely decoupled from the other, less malleable layers of the composition. Quite the contrary: Boulez’s creative decisions always show a tendency to be influenced by the characteristics of the material he works with.(23)
Example 11. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, prime form of fφ
(click to enlarge)
[2.14] As an example, let us return to the beginning of the piece (mm. 1–15, Example 2 and Example 3), where we found a process of gradual minor third and then tritone convergence within the harmonic fields. Dodecaphonically, each instrumental group plays two consecutive forms of the twelve-tone row fφ while the individual pitches are distributed between the instruments of each group. The prime form of fφ is given in Example 11.
[2.15] The most frequent interval succession within the row is the minor third, followed by an even split of two major seconds, major thirds, fourths, and tritones; the minor second is missing. Taking a closer look, one can identify a symmetry concerning the tritone and minor third connections—the minor third B–
Example 12. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, mm. 1–15, transpositions of fφ(I) per instrumental group (numbered 1–7, group 6 being silent); the table indicates the first pitch class of each transposition
(click to enlarge)
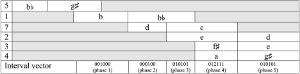
[2.16] Each row form in this section is a transposition of the inverted prime form. Consequently, when two row forms of fφ are played simultaneously, the interval between the row forms is likely to be prominent, as will be certain intervals within each individual row. Instead of tracing the complex and experimental procedure Boulez used to generate and distribute these row forms, let us just have a look at the outcome. Example 12 shows which two transpositions appear in each group (numbered 1–7, group 6 being silent) and how they overlap.
[2.17] We can follow the interval vectors to see which intervals appear between the overlapping row forms in each phase: The first two overlapping forms of fφ (phase 1) are a minor third apart leading to a simple interval vector of <001000> (0 minor seconds, 0 major seconds, 1 minor third etc.), the next two are a major third apart (phase 2). The tritone interval between two forms appears in phases 3–5. In phase 4 it results from the double minor-third constellation between the transpositions on
[2.18] The characteristics of the harmonic fields are thus mirrored in the underlying structure of pitch organization. Within the twelve-tone row, there is a symmetrical distribution of minor thirds and tritones, and minor thirds are statistically prominent. Between rows, there are tritones subdivided by minor thirds, followed by tritones without minor thirds.
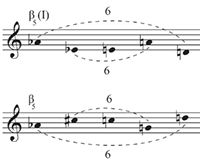
[2.19] Similar observations can be made for the tritone harmony at the beginning of the slow section (mm. 75–79, Example 9 and Example 10). This section uses only two forms of the twelve-tone row β consecutively per instrumental group. That means the same two row forms are played (more or less) simultaneously between all groups. Not only that: the content of both row forms is reduced to only one subset of five pitch classes, the other seven pitch classes being omitted.
Example 13. Pierre Boulez, Polyphonie X, segments of β5(I) and β5 used in mm. 75–79
(click to enlarge)
[2.20] First, on a very abstract level, this reduction is caused by a tritone constellation within another “hidden” row: Boulez uses certain intervals within these hidden rows and their inversions to generate a selection of (still hidden) transpositions that then, using yet another algorithm, lead to the actual row forms.(24) In this system, a tritone (being identical with its inversion) results in two identical row forms being used. Boulez then decided to split those two row forms into two segments, using only one segment in this section. These two partial row forms are once again characterized by tritone symmetry, similar to what we observed in fφ; see Example 13.
[2.21] Logically, the inversion of β5 has the same interval structure as the original form, which is characterized by a symmetrical distribution of two tritones around a central mirror axis. This leads to a duplication of not only the first but also the fifth pitch class in each of the two forms. The overall pitch content is thus reduced to eight different pitch classes instead of the usual twelve.
[2.22] Boulez now seems to react to the structural significance of the tritone in two ways. First, he distributes the contents of each row segment to the instruments in such a way that the tritone connections are played melodically within a single instrument (as shown in Examples 3 and 4 above). Second, as we have seen, he distributes the registers in such a way that these tritones appear in close position, with the two axis pitch classes without a tritone complement (E and C) being pushed to the low register in an open position (as a sixth).
[2.23] In sum, the examples above shed light on the importance of registral distribution in Boulez’s harmonic thinking. Pitch registration is used a mediating layer between the more hidden organizational structures and the sounding musical surface. A statistical accumulation of certain key intervals bears potentials for the listening experience without aiming at full transparency or even identity between the structural and formal characteristics of a piece. It is used as a means of compositional agency toward musical “form” and is at the same time influenced by its generative “structures.” The following examples will pursue this idea further, applying harmonic field analysis to post-serial compositions by Marco Stroppa and Yukiko Watanabe.
3. Marco Stroppa: Hommage à Gy. K. (1997–2003, rev. 2013)
[3.1] Field structures with specific registral distributions have been an integral part of Marco Stroppa’s compositional technique since the 1988 string quartet Spirali.(25) Stroppa combines two elements in his works: gestures with relative morphological conciseness, which Stroppa calls OIM (organismi di informazione musicale),(26) and harmonic fields, which Stroppa calls vertical pitch structures (VPS).(27) Both are typically subjected to a constant process of transformation and interfere with each other in different ways.
[3.2] The piece Hommage à Gy. K. for clarinet, viola, and piano was composed between 1997 and 2003. It is both a first– and second-order homage: the title refers directly to György Kurtág’s Hommage à R. Sch. (1990), and both Stroppa and Kurtág incorporate elements from Robert Schumann’s Märchenerzählungen op. 132 (1853), whose instrumentation they also adopt.
[3.3] Characteristic of the first movement of Stroppa’s Hommage is an ascending sixteenth-note gesture in the piano that is repeated twenty-seven times and is constantly transformed; Example 14 highlights its initial eight occurrences. It resembles the sixteenth-note figure from the first movement of Kurtág’s Hommage, shown in Example 15. Whereas in Kurtág the chromatic band is constantly divided into three segments with a fixed registral distribution (3 + 2 + 3) so that each segment melodically reproduces a chromatic scale section, in Stroppa both the segmentation and the registration are subject to continuous change.
Example 14. Marco Stroppa, Hommage à Gy. K., first movement, mm. 1–8 (click to enlarge and see the rest) | Example 15. György Kurtág, Hommage à R. Sch., first movement, transcription of the initial sixteenth-note motive in the clarinet, m. 1, notation in C (click to enlarge) |
Example 16. Marco Stroppa, Hommage à Gy. K., first movement, pitch class sequences and harmonic fields of every occurrence of the piano motive
(click to enlarge and see the rest)
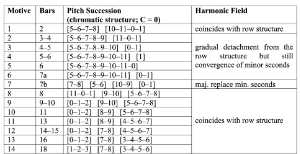
[3.4] The third column of Example 16 shows the pitch-class sequences for all twenty-seven repetitions of the motive (0 = C; 1 =
Example 17. Marco Stroppa, Hommage à Gy. K., first movement, harmonic fields of the first 7 instances of the piano motive
(click to enlarge)
[3.5] The vertical registral distribution now creates a second dramatic layer that interferes with these horizontal, row-like sequences.(28) Instead of realizing the chromatic relations in close registral position throughout, the harmonic fields tend to overwrite the chromatic sequences. In the first seven measures, a gradual detachment of the harmonic fields from the pitch-class sequences can be observed (Example 17). After complete congruence in the first occurrence of the motive, additional minor-second constellations emerge solely through the pitch distribution across registers. This detachment process culminates in m. 7, where the minor second is completely erased and replaced by major-second constellations (Example 17, instance 7). One could say that the diatonic flair of the major second pushes itself in front of the chromaticism of the nominal pitch-class relationships and asserts its own priority.
Example 18. Marco Stroppa, Hommage à Gy. K., first movement, harmonic fields of instances 8–14 of the piano motive
(click to enlarge and see the rest)
[3.6] Measures 8–18 then abruptly restore the initial congruence between pitch-class sequences and harmonic fields, which, at least for me, makes it easier to follow the subtle shifts within the sequences. The lowest pitch gradually rises from B3 to
Example 19. Marco Stroppa, Hommage à Gy. K., first movement, harmonic fields of instances 15–27 of the piano motive
(click to enlarge and see the rest)
[3.7] The second half of the movement (mm. 19–38) takes the dissolution of the chromatic relationships to the extreme. In m. 29, minor and major thirds overwrite the minor seconds, similarly to what has happened in m. 7 (Example 19, instance 21); from m. 31, the fields gradually spread out over the entire ambitus, isolating each individual note in frequency. Only at the very end (m. 38) do the minor seconds reappear in a quasi-recapitulatory manner. But they belong to different segments within the pitch-class sequence and therefore do not appear melodically. Generally, from m. 29 onward, minor seconds in direct melodic succession are completely avoided; see Example 19.
Example 20. Kentaro Taki, Living in the Box (2012), screenshot of the video material that is reused in Yukiko Watanabe’s Living in the Box II (by courtesy of Mori Yu Gallery)
(click to enlarge)
[3.8] One can conclude that the juxtaposition of horizontal and vertical pitch organization (or, in other words, pitch-class sequence and pitch registration) in the first movement of Stroppa’s Hommage enables a play with the structural and formal function of the minor second that is similar to the role of the tritone in Polyphonie X. In both cases, harmonic fields oscillate between convergence and dissolution, continuity and discontinuity, and perceptibility and virtuality.
4. Yukiko Watanabe: Living in the Box II (2013)
[4.1] Living in the Box II is a collaboration between the Japanese composer Yukiko Watanabe and the video artist Kentaro Taki. During the ten-minute piano piece, a surreal video projection shows female-read body parts in differently sized white boxes (see Example 20).(29) Along with the live performance of the pianist, these body parts appear, disappear, stretch, and move within these boxes without any clear direction.
Example 21. Yukiko Watanabe, Living in the Box II, mm. 1–4.
(click to enlarge)
[4.2] This fractured imagery is paralleled by the music. The pianist first repeats an unwinding 24-note sequence several times (Example 21).(30) This figure—which Diego Ramos (2021, 113) notes is like a Möbius strip—is at the same time one of three main pitch structures that organize the piece (I will call them A, B, and C respectively).(31) In the first section after its full exposition (mm. 2–26), the sequence (identical with generative structure A) is radically de- and reconstructed: the pianist keeps moving their fingers over the keys as if they would continue repeating the sequence, but only some of the notes (those with open noteheads) are actually played, beginning with only a couple and then gradually increasing the density of actual sounds.
Example 22. Yukiko Watanabe, Living in the Box II, harmonic fields A, B, and C
(click to enlarge)
[4.3] Like Stroppa’s piece, the pitch sequence is chromatically organized; as one can easily see, it traverses the full chromatic scale twice beginning with C,
[4.4] Interestingly, the harmonic fields do not mirror the nominal chromaticism by emphasizing minor seconds (like, as shown above, many fields in Stroppa do) but rather complement it from the outset with diatonic constellations of major seconds and minor/major thirds. In structure A, for example, these constellations can be grouped into four auditory streams of consistent diatonic scales, the lowest six pitches all belonging to the
[4.5] Using only structure A, the first section of the piece (mm. 1–26) consists of a static, single harmonic field with the above-mentioned diatonic characteristics. While it is certainly possible to perceive the chromaticism of the sequence when it is repeated in the beginning, my own attention, in accordance with Bregman’s theory, tends to shift toward these quasi-tonal streams and constellations. When most of the notes are muted during the rest of the section, the chromaticism is entirely virtual, uncovering the diatonicism of the harmonic fields and making it possible to follow these relations without distraction.
Example 23. Yukiko Watanabe, Living in the Box II, mm. 71–74
(click to enlarge)
[4.6] In the second section (mm. 27–74), all three structures A, B, and C are combined. This leads to occasional minor-second constellations due to their complementary registral distributions (for example B2–
Example 24. Yukiko Watanabe, Living in the Box II, mm. 75–82 (click to enlarge) | Example 25. Yukiko Watanabe, Living in the Box II, mm. 105–7 (click to enlarge) |
[4.7] The overall arc of the piece can thus be described as an ABA' form, with registral distribution being the driving force and most prominent feature of this arc. However, it is noteworthy that the pitch organization in Living in the Box II, with its arc of harmonic de- and reconstruction, also contributes to a conceptual idea of the piece: it accentuates the bodily movements of the performer along the lines of the deconstructed body shown in the video.(33) Ramos (2021, 114) states: “The fact that there are three arpeggio layers for two hands creates a virtuosic choreography with continuous leaps and hand-crossing that is reminiscent of works by Franz Liszt.” In some renditions of the piece, the video projection is even projected on the back of the pianist to accentuate this idea of musical embodiment. Harmonic fields are thus used to not only create musical form and drama but also with awareness of their consequences for the performance: while the piece explores the continuum between temporarily isolated and accumulated sounds on the one hand, as well as spatially close and distant sounds on the other, the mediated corporeal presence of the performer also becomes a part of the composition.
5. Conclusion
[5.1] The methodology of harmonic field analysis presented in this paper was designed to solve a specific problem: it is meant to uncover harmonic colorings with recurring interval constellations, relative pitch frequency, or register continuity that result from the choice of registers in serial music. In this sense, it is a continuation of the work of Jean-Louis Leleu that, instead of focusing on interval cycles, emphasizes the statistical accumulation of key intervals. This shift of perspective is informed by psycho-acoustical findings within the orbit of Bregman’s auditory stream analysis.
[5.2] As shown in the discussions of composers from three different generations, harmonic field analysis is able to reveal a middle layer between the sounding surface and its underlying generative principles: harmonic fields are mediating structures with strong potentials for perception.(34) In the first movement of Boulez’s Polyphonie X, they create a drama of tritone convergence (and deconstruction) that characterize the sections of the piece in different ways. Similarly, in the first movement of Marco Stroppa’s Hommage à Gy. K., minor-second constellations highlight the chromatic structure of the main motive until they become gradually detached and finally completely suspended. Lastly, Yukiko Watanabe’s piece Living in the Box II also uses structural chromaticism while simultaneously confronting it with contradictory harmonic fields consisting of quasi-tonal, diatonic auditory streams. Harmonic field analysis is a useful tool to uncover these structural-formal entanglements.
Simon Tönies
Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen
Institut für Musikwissenschaft und Musikpädagogik
Karl-Glöckner-Str. 21 D
35394 Gießen, Germany
simon.toenies@musik.uni-giessen.de
Works Cited
Albert, Giacomo. 2019. “Von der Immersion zur Dramaturgie: Klang, Form und Visualität bei Marco Stroppa.” Musik-Konzepte 186: 30–43.
Boulez, Pierre. [1963] 2011. Penser la musique aujourd’hui. Gallimard.
—————. [1952] 1991. “Possibly
—————. [1954] 1991. “‘
—————. 1952. Letter to Henri Pousseur of March 1952. Manuscript archived in the Paul Sacher Foundation, Bâle, collection Henri Pousseur.
Bregman, Albert. 1994. Auditory Scene Analysis: The Perceptual Organization of Sound. MIT Press. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.408434.
Decroupet, Pascal. 2019. “Zeit — Harmonik — Klang: Figurenwelt und Klangtechnik in Marco Stroppas ‘Moai&rsquo und Hiranyaloka.&rdquo Musik-Konzepte 186: 44–62.
Deutsch, Diana. 2012. “Grouping Mechanisms in Music.” In The Psychology of Music, ed. Diana Deutsch, 183–248. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-381460-9.00006-7.
Dubiel, Joseph. 1997. “What’s the Use of the Twelve-Tone System?” Perspectives of New Music 35 (2): 33–51. https://doi.org/10.2307/833641.
Forte, Allen. 1973. The Structure of Atonal Music. Yale University Press.
Goldman, Jonathan. 2011. The Musical Language of Pierre Boulez: Writings and Compositions. Cambridge University Press.
Grisey, Gérard. 1987. “Tempus ex Machina: A Composer’s Reflections on Musical Time.” Contemporary Music Review 2 (1): 239–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/07494468708567060.
Latour, Bruno. 2005. Reassembling the Social: An Introduction to Actor-Network-Theory. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780199256044.001.0001.
Leibowitz, René. 1947. Schœnberg et son école. J. B. Janin.
Leleu, Jean-Louis. 2015. “Cellules rythmiques et développement organique: la fonction des champs harmoniques dans le mouvement IIIb du Livre pour quatuor de Pierre Boulez.” In La construction de l’idée musicale: Essais sur Webern, Debussy et Boulez, 387–406. Contrechamps. https://doi.org/10.4000/books.contrechamps.2356.
Lerdahl, Fred. 1992. “Cognitive Constraints on Compositional Systems.” Contemporary Music Review 6 (2): 97–121.
Ligeti, György. 1958. “Pierre Boulez. Entscheidung und Automatik in der Structure Ia.” Die Reihe 4: 38–63.
Losada, Catherine. 2019. “Middleground Structure in the Cadenza to Boulez’s Éclat.” Music Theory Online 25 (1). https://doi.org/10.30535/mto.25.1.4.
—————. 2014. “Complex Multiplication, Structure, and Process: Harmony and Form in Boulez’s Structures II.” Music Theory Spectrum 36 (1): 86–120. https://doi.org/10.1093/mts/mtu005.
McAdams, Stephen. 2012. “Musical Timbre Perception.” In The Psychology of Music, ed. Diana Deutsch, 35–67. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-381460-9.00002-X.
Mosch, Ulrich. 2004. Musikalisches Hören serieller Musik: Untersuchungen am Beispiel von Pierre Boulez’ Le Marteau sans maitre. Pfau.
Nakamura, Rei. 2013. Video documentation of a performance of Living in the Box II by Yukiko Watanabe at the Piano+ Festival Karlsruhe. ZKM, Institut für Bildmedien. https://vimeo.com/99947888. Accessed April 20, 2024.
Peles, Stephen. “‘Ist Alles Eins’: Schoenberg and Symmetry.” Music Theory Spectrum 26 (1): 57–86. https://doi.org/10.1525/mts.2004.26.1.57.
—————. 1983/84. “Interpretation of Sets in Multiple Dimensions: Notes on the Second Movement of Arnold Schoenberg’s String Quartet #3.” Perspectives of New Music 22 (1/2): 303–52. https://doi.org/10.2307/832952.
Perle, George. 1977. Twelve-Tone Tonality. University of California Press.
Piencikowski, Robert. 1985. “Nature morte avec guitare.” In Pierre Boulez: Eine Festschrift zum 60. Geburtstag, ed. Josef Häusler, 66–81. Universal Edition.
Ramos, Diego. 2021. “Notation and Performance Practice in Works for Piano and Audiovisual Media.” In Movement to Sound, Sound to Movement: Interpreting Multimedia Piano Compositions, ed. Rei Nakamura, Marion Saxer, and Simon Tönies, 103–20. Wolke.
Salem, Joseph. 2017. “The Integrity of Boulez’s Integral Serialism: Polyphonie X and Musical Failure as Compositional Success.” Contemporary Music Review 36 (5): 337–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/07494467.2017.1401366.
—————. 2016. “Serial Processes, Agency and Improvisation.” In Pierre Boulez Studies, ed. Edward Campbell and Peter O’Hagan, 221–45. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107477216.010.
Strinz, Werner. 2016. “‘Du fond d’un naufrage&rsquo: The Quarter-tone Compositions of Pierre Boulez.” In Pierre Boulez Studies, ed. Edward Campbell and Peter O’Hagan, 139–70. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107477216.007.
Stroppa, Marco. 1989. “Organismes d’information musicale: une approche de la composition.” In La musique et les sciences cognitives, ed. Stephen McAdams and Irène Deliège, 203–32. Pierre Mardaga.
Taki, Kentaro. 2012. Living in the Box. Video installation. Mori Yu Gallery.
Thomson, William. 2010. “Serialist Claims versus Sonic Reality.” Empirical Musicology Review 5 (2): 36–50. https://doi.org/10.18061/1811/46748.
Tiffon, Vincent, and Noémie Sprenger-Ohana. 2012. “The Creative Process in Traiettoria: An Account of the Genesis of Marco Stroppa’s Musical Thought.” Contemporary Music Review 30 (5): 377–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/07494467.2011.665580.
Tönies, Simon. 2023. Ins Unbekannte. Technik und Ästhetik in Pierre Boulez’ Polyphonie X. Wolke.
Utz, Christian. 2017. “Zum performativen Hören serieller Musik: Analyse und Aufführung von Pierre Boulez’ Structures Ia (1951) und Polyphonie X (1951).” In Wider den Fetisch der Partitur: Hörprobleme serieller und post-serieller Musik, ed. Susanne Kogler and Martin Zenck. Schott Campus. https://schott-campus.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/IV.4-05-Utz.pdf. Accessed August 7, 2021.
—————. 2013. “Entwürfe zu einer Theorie musikalischer Syntax: Morphosyntaktische Beziehungen zwischen Alltagswahrnehmung und dem Hören tonaler und posttonaler Musik.” In Musik-Sprachen: Beiträge zur Sprachnähe und Sprachferne von Musik im Dialog mit Albrecht Wellmer, ed. Christian Utz, Dieter Kleinrath, and Clemens Gadenstätter, 61–101. Pfau. https://doi.org/10.25366/2023.75.
—————. 2012. “Struktur und Wahrnehmung. Gestalt, Kontur, Figur und Geste in Analysen der Musik des 20. Jahrhunderts.” Musik & Ästhetik 64: 53–80.
Watanabe, Yukiko. 2021. Work description for Living in the Box II. In Movement to Sound, Sound to Movement: Interpreting Multimedia Piano Compositions, ed. Rei Nakamura, Marion Saxer, and Simon Tönies, 244–45. Wolke.
Zenck, Martin. 2015. “Pierre Boulez: Polyphonie X (1951): Ein gescheitertes, weil zurückgezogenes Werk; ein ‘tombeau à tête reposée’?” Archiv für Musikwissenschaft 72: 277–301. https://doi.org/10.25162/afmw-2015-0015.
Footnotes
1. For lack of better, less problematic alternatives, I use the term “structure” to denote the different layers of organization that contribute to the sounding outcome of a musical text, and “form” to denote the sounding outcome of a musical text and its perceptible features and/or processes.
Return to text
2. See, for example, Thomson 2010.
Return to text
3. In his critique of system-oriented analytic approaches, Joseph Dubiel (1997, 44) concedes the possibility of “hearing the influence of the series” but at the same time marginalizes the system’s agency, concluding “how little the system specifies about the configurations that will occur, and how discontinuous and unpredictable the system’s interpretative influence is likely to be, when it can be felt” (49). Against such viewpoints, Catherine Losada (2014, 118) stresses the “importance of a precise understanding of the interaction between precompositional schemes and the ultimate musical product at all stages of the work.”
Return to text
4. See Boulez [1954] 1991, 156.
Return to text
5. The close curation of the whole registral space is typical for post-war serialism, where traditional voice leading in melodic lines is frequently suspended. However, register choice already plays an important role in the Second Viennese School—see for example Stephen Peles’s (1983/84; 2004) analysis of symmetrical register dispositions in Schoenberg.
Return to text
6. By “post-serial” I mean compositional approaches that either use generative background structures or apply algorithmic procedures to a given musical material.
Return to text
7. In the mid-eighties, Piencikowski was concerned with placing innovations such as the mixture sounds in Boulez’s Eclat-multiples in a broader context by revealing their roots in serial thinking. In this way, he turns against interpretations that see in it a radical shift of the composer from “structural” to perception-oriented composing. (I thank Pascal Decroupet for this contextualization.)
Return to text
8. Utz cites studies by Diana Deutsch, Albert S. Bregman, Eleanor Rosch and Irène Deliège.
Return to text
9. For an overview, see Deutsch 2012, 196–200.
Return to text
10. Individual listening history is likely to have a decisive influence on the outcome of such a study. If perception is not simply passive registration of a stimulus but must be imagined as a dynamic-cyclical process between subject and object (see the remarks in Mosch 2004, 123–145), an analysis can only ever reveal potentials of the same.
Return to text
11. Compare Perle 1977, 18–19, 76–79.
Return to text
12. See Forte 1973.
Return to text
13. Boulez, autograph letter to Henri Pousseur, March 1952, 156, Paul Sacher Foundation, Bâle, collection Henri Pousseur.
Return to text
14. In light of these considerations, we have to reconsider statements that assume a sudden shift toward perception in the 1970s, such as Jonathan Goldman’s (2011, 61–62): “Boulez’s discourse in the Collège de France lectures provides evidence of a fairly dramatic about-face: he had clearly begun to include the listener in the realm of his
Return to text
15. During his formative years, Boulez was influenced by René Leibowitz, who familiarized him with the music of Schoenberg, Berg, and Webern. Despite their quarrel in 1946, Boulez had certainly read Leibowitz’s 1947 treatise Schoenberg et son école, which repeatedly addresses Webern’s use of fixed or mobile pitch registration. For example, regarding the second movement of Op. 28, Leibowitz reproduces a vertical pitch structure that strongly resembles the interlocking thirds and tritones that we will encounter in the first movement of Polyphonie X (1947, 251).
Return to text
16. See Tönies 2023, 30–35. Recent studies on Polyphonie X include Salem 2017; Strintz 2016; and Zenck 2015. After its premiere in Donaueschingen, Boulez decided to withdraw Polyphonie X from his work catalogue.
Return to text
17. See Tönies 2023, 80–95.
Return to text
18. The sketches are archived in the Paul Sacher Foundation, collection Pierre Boulez, folder C, 1a.
Return to text
19. Especially the three slow sections (mm. 75–96, 160–69, and 209–27).
Return to text
20. On the role of timbre in auditory streaming see McAdams 2012, 50–52.
Return to text
21. See Example 10 for a complete reproduction of mm. 75–80.
Return to text
22. A full overview of the underlying serial structure is not possible within the scope of this article. For a systematic reconstruction of the compositional process, see Tönies 2023. Polyphonie X is Boulez’s first attempt to deduce a piece entirely from a single basic row that proliferates in various and complex ways. The other musical dimensions like rhythm, dynamics, articulation, timbre, etc. are autonomous systems, each following their own logic and being subsequently applied to the serial macrostructure. In contrast to his later works, where compositional control is reintroduced on the level of material disposition, this clash of distinct musical parameters is highly unpredictable and creates unforeseeable outcomes.
Return to text
23. This tendency is especially apparent in the many revisions and re-compositions in Boulez’s output—see, for example Losada 2019 and Salem 2016, 232–245.
Return to text
24. See Tönies 2023, 64–67, 99–101.
Return to text
25. See Albert 2019, 41. On the importance of cognitive sciences and psychoacoustics for Stroppa’s musical thinking, see Tiffon and Sprenger-Ohana 2012, 390–391.
Return to text
26. Stroppa explains the concept of OIM in his essay “Organismes d’information musicale: une approche de la composition” (1989).
Return to text
27. For an exemplary analysis of vertical pitch structures in Stroppa’s piano cycle Miniature estrose, see Decroupet 2019.
Return to text
28. Only the piano motive as an entity is considered in the following analysis. A more in-depth view should also take into account the subtle resonance sounds created by the sustain pedal as well eventual octave shifts in the accompaniment.
Return to text
29. The video reuses material from the (2012) installation Living in the Box by Kentaro Taki.
Return to text
30. Even though the score indicates that these eight initial repetitions should be played silently, Watanabe tends to contradict this indication for live renditions of the piece. A video documentation of a performance by Rei Nakamura can be found online: https://vimeo.com/99947888 (accessed August 7, 2021).
Return to text
31. I thank Yukiko Watanabe for providing me drafts concerning the serial organization. In addition to the three main pitch structures, a fourth structure is used that governs the use of harmonics (plucked strings).
Return to text
32. See also Ramos 2021, 113–116. In the drafts, these structures contain additional information on rhythmic durations and dynamics that are developed in different ways during the piece.
Return to text
33. Watanabe (2021, 244–245) says: “Like the body parts in the video, I was seeking an expression that brings the beauty of the pianist’s body to light even in the smallest muscular movements.”
Return to text
34. Similarly, Losada (2019, 24) demonstrates how, in works like Eclat, “Boulez was concerned with creating a perceptible middleground organization” that iterates harmonic characteristics of the basic material.
Return to text
Copyright Statement
Copyright © 2024 by the Society for Music Theory. All rights reserved.
[1] Copyrights for individual items published in Music Theory Online (MTO) are held by their authors. Items appearing in MTO may be saved and stored in electronic or paper form, and may be shared among individuals for purposes of scholarly research or discussion, but may not be republished in any form, electronic or print, without prior, written permission from the author(s), and advance notification of the editors of MTO.
[2] Any redistributed form of items published in MTO must include the following information in a form appropriate to the medium in which the items are to appear:
This item appeared in Music Theory Online in [VOLUME #, ISSUE #] on [DAY/MONTH/YEAR]. It was authored by [FULL NAME, EMAIL ADDRESS], with whose written permission it is reprinted here.
[3] Libraries may archive issues of MTO in electronic or paper form for public access so long as each issue is stored in its entirety, and no access fee is charged. Exceptions to these requirements must be approved in writing by the editors of MTO, who will act in accordance with the decisions of the Society for Music Theory.
This document and all portions thereof are protected by U.S. and international copyright laws. Material contained herein may be copied and/or distributed for research purposes only.
Prepared by Leah Amarosa, Editorial Assistant
Number of visits:
4436